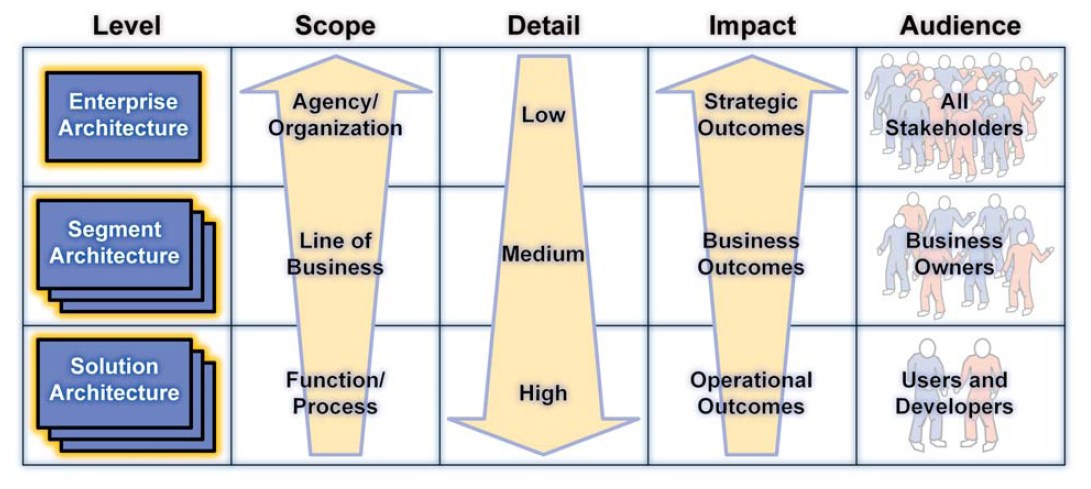
Solution Architecture Management
Solution Architecture Management refers to the governance processes and disciplines for guiding architecture decisions and enforcing technology standards throughout the design, delivery, and evolution of complex enterprise IT solutions. It ensures solution architectures - represented through models, principles, specs and other artifacts - remain living assets providing sustained business value.
Core activities span managing architecture dependencies, aligning designs to capability roadmaps, providing oversight into development tradeoffs impacting architectures, as well as maintaining integrity of architecture artifacts over time. Robust review cycles, configuration control, and effective communication of architecture changes are also critical.
With solutions becoming interconnected across domains, architecture management provides strategic insight and control to balance agility demands while minimizing enterprise risk, highlighting the importance of enterprise solution strategy.
Having skilled architecture managers who can synthesize business contexts along with technical intricacies is key for enterprises looking to sustain growth of solution portfolios.
What is solution architecture management?
Solution architecture management refers to the discipline focused on governing solution architecture decisions and activities throughout the design, delivery, and ongoing enhancement of complex enterprise IT solutions. It ensures solution architectures which serve as the blueprint for guiding development remain aligned with business objectives and technical standards over time.
Core responsibilities span managing architecture dependencies, providing oversight into proposed design changes, reviewing project deviation requests, maintaining integrity of architecture artifacts, identifying reuse opportunities, sustaining alignment to capability roadmaps, and communicating architecture changes across governance boards.
With solutions becoming interconnected across domains, architecture management provides that strategic insight and control to balance agility demands while minimizing enterprise risk that comes with uncontrolled diversity.
Equipped with consistent processes, gating mechanisms and centrally managed architecture repositories, architecture management aims to sustain solution quality and coherence as complexity continues expanding for most organizations.
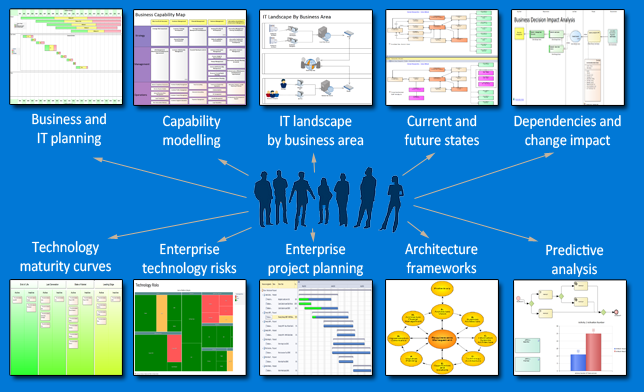
What are the benefits of a solution architecture management?
Implementing robust enterprise architecture management practices is crucial for software development projects, where the project manager collaborates closely with the enterprise architect for success. solution architecture management practices brings several advantages for enterprises managing large solution portfolios. It enables centralized visibility into solution designs across domains, minimizing redundancies and promoting reuse. Standard compliance reduces costs of integration and is a fundamental aspect of enterprise architecture, necessitating the architect must prioritize it.
Planned governance procedures improve the quality of architecture artifacts over time and across programs. With executive oversight into architecture decisions, mismatches between business priorities and technical implementations get quickly identified allowing course corrections.
Architecture management also assures long-term viability of solutions by establishing ongoing processes to evolve designs adapting to new technologies or integration needs. Another benefit is increased solution lifecycle stability from controlled change management and version control capabilities, crucial in software development.
Furthermore, new project teams can rapidly onboard and orient themselves on system contexts through access to governing architecture collateral maintained in repositories, a testament to the architect role in project management. By institutionalizing architecture management, organizations can scale technology solution portfolios efficiently while keeping complexity in check.
What are the key features of a solution architecture management?
Core features of robust solution architecture management implementations include establishment of architecture review boards who oversee governance procedures, centralized repositories containing authoritative architecture artifacts and metadata, structured architecture processes aligned to solution lifecycle stages, integrated tooling that links architecture models to downstream development activities, and dashboards for relevant stakeholders to provide visibility into governance artifacts including architecture health metrics and decisions.
Standard templates and modeling conventions ensure quality and consistency of architecture deliverables. Formal review and approval processes powered by workflows focus on assessing architecture deviations, managing change requests and risk dependencies.
Communication plans aid awareness of architecture changes enterprise-wide. Version control, roadmap linkage, and configuration audits further strengthen governance capabilities. Rather than adhoc oversight, integrated architecture management capabilities institutionalize systematic governance across solution portfolios, aligning architectures to business objectives while creating accountability for architecture quality - thus taming complexity at scale.
How important is a solution architecture management?
Solution architecture management Enterprise architecture is critically important for enterprises undergoing large-scale digital transformation powered by interconnected technology solutions. With growing complexity, rapidly changing needs, and solutions spanning domains, lack of architecture oversight introduces substantial delivery risks and rising costs from duplicative or disjointed systems.
Alternatively, disciplined governance ensures solution architectures remain trusted and living blueprints that align to business objectives. Management control enables planned innovation by identifying reuse potential. It also assures stability minimizing disruption when enhancing existing mission-critical solutions.
From assessing proposed architectural changes and reviewing project deviation requests to maintaining roadmap linkage, architecture management powers impact analysis across solution portfolios - leveraging architectures as centralized knowledge hubs. Its auditing strengthens compliance, an aspect where the enterprise architect plays a key role in ensuring enterprise architecture aligns with legal and regulatory standards.
For these reasons, mature IT organizations regard capable architecture management functions as pivotal for harnessing complexity, assuring solution integrity over lifetimes, and scaling innovations - making it a strategic imperative.
Who needs a solution architecture management?
As enterprises embrace digital transformation, the breadth and interconnectedness of technology solutions grow rapidly, making solution architecture management crucial for companies struggling with complex, disjointed solution portfolios.
Leading organizations needing architecture oversight typically have multidomain solutions, numerous distributed teams, and existing legacy systems being enhanced continuously, a scenario demanding seasoned architecture management and project management expertise. Rapid growth and mergers also drive complexity.
Companies undergoing cloud migration require management to ensure solutions leverage cloud native patterns. Startups building innovative platforms need governance to promote extensibility and scale. Government agencies have to demonstrate architecture compliance. Additionally, sectors with ecosystem integration like healthcare sharing patient data depend on mature architecture capabilities when interconnecting disparate systems.
Across contexts, architecture management is pivotal where business priorities, diverse technologies and shared data/infrastructure intersect. It enables CIOs to implement guardrails as solution diversity expands.
For technology leaders guiding large, business-critical portfolios, investing in architecture management ultimately allows innovation speed to increase while reducing enterprise risk profile, a task for the enterprise architect.
Best practices of solution architecture management
Leading solutions architecture management practices involve establishing an architecture review board consisting of multi-disciplinary stakeholders who oversee governance procedures and decisions. Another critical practice is creation of a centralized architecture repository containing authoritative visual models, principles, specs and metadata to provide single source of truth.
Standard architecture processes need integration with development and project lifecycles via formal reviews for changes, reuse potential, risk, deviations and retirement. Easy accessibility of artifacts for reference and impact analyses promotes usage. Mapping business capabilities to solution components sustains alignment. Sandbox environments facilitate what-if exploration, a technique often used in software development to test specific solutions without impacting the actual enterprise architecture.
Automation of governance workflows and assessments enhances consistency, while dashboards and KPIs give visibility enabling data-driven oversight. Promoting architecture-centric thinking across teams through informal architecture clinics and guides helps adoption.
With these comprehensive capabilities integrated, architecture management shifts from ad-hoc to a systematic capability for sustained assurance of solution integrity, quality and business technology synergy as complexity scales.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Solution Architect Manager
A Solution Architect Manager holds an important leadership role responsible for establishing and maintaining effective architecture management across complex enterprise IT solution portfolios, underscoring the architect role in guiding enterprise architecture.
Key responsibilities include creating and upholding architecture processes/standards, facilitating major architecture decisions through structured review boards, maintaining architecture repositories as living assets. Driving communication on architecture changes and providing oversight into solution designs end-to-end, an enterprise architect must ensure alignment with enterprise architecture objectives. Assessing architecture health via governance KPIs, and ensuring continuity with business vision and capability roadmaps. They serve as the architecture conscience nurturing a culture focused on architecture quality.
As chief architect, they lead continuous evaluations of emerging technologies for adoption while seeking opportunities to consolidate duplicative systems. With deep technical knowledge and soft skills to coordinate across programs, they continually balance enterprise agility demands with risks from architectural erosion. Their broad vantage point is crucial for CIOs to scale technology investments securely, demonstrating the critical role of a solution architect in strategic planning.
The multifaceted responsibilities make the Solution Architect Manager integral to governing solution portfolios as they grow extensively, embodying the role of a solution architect in enterprise architecture.
